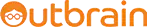On-page Vs. Off-page SEO [Checklists Included]
Everyone wants their website to rank on the first page of Google, but getting there takes a lot more effort than you initially thought. For starters, you need to understand the basics of SEO, on-page vs. off-page SEO.
In this blog post, I’ll take you through on-page and off-page SEO, their differences, and other key elements of search engine optimization you need to know to get your site ranking.
Table of Contents
Difference Between On-page and Off-page SEO
Google Ranking Factors for On-Page SEO
Google Ranking Factors for Off-Page SEO
- Link Building
- Guest Blogging
- Broken Link Reclamation
- Infographics Distribution
- Social Media Links
- Google My Business (GMB)
- Reviews

What is On-page SEO
On-page SEO is a set of activities you perform on your site for better search engine optimization. These activities include,
- Internal linking
- Meta tags optimization
- Keyword optimization
- Page speed optimization
- Alt text optimization
And much more.
These activities improve your site’s user experience and search engine rankings. This is because search engines recommend websites optimized for web visitors. When your site is delightful, Google and other search engines will value it over other sites ranking for similar keywords.
Website On-page SEO Audit
Website on-page SEO audit is the process of checking the backend elements of your website. These elements include meta title, meta description, heading tags (H1, H2), website copy, website structure, canonicalization, and many more on-page elements.
Running an on-page SEO audit is the first step of on-page optimization. Here’s our on-page SEO checklist you can use.
Google Ranking Factors for On-Page SEO
Google evaluates websites against hundreds of ranking factors, making it almost impossible to aim your SEO strategy in the right direction. But what we do know is that Google is looking for awesomeness.
To achieve Google’s level of awesomeness, you have to break through the noise of 1.9 million + websites and shine like a star.
So far, we know that Google is constantly improving its ranking factors. This means newer updates have roots in the old algorithm. So, with a little creativity, you can rank your website against your target keywords.
However, to do that, you need to understand Google’s ranking factors for On-page SEO. Because if your website isn’t delightful for your visitors, Google won’t bother ranking it against your keywords.
Here are some of the most impactful Google ranking factors for On-page SEO. Once you master them, you are halfway to your target rank on SERPs.
1. Core Web Vitals
Core web vitals are a set of metrics that quantify your site’s user experience. These metrics include visual stability, page load time, and interactivity. Focusing on these metrics gives your site an edge over your competitors.
Moreover, constantly evolving and improving your core web vitals, signals that your site is active, up-to-date, and has a positive user experience. Here’s a brief explanation of all three core web vitals
LCP (Load time)
LCP stands for Largest Contentful Paint. It’s the largest-sized image on your web, and Google takes note of its load time on your site. The faster your LCP loads(less than 2.5 seconds), the better for your page. Websites that aren’t optimized to the latest standards often have a high LCP, adversely affecting their rankings.
FID (Interactivity)
FID stands for First Input Delay. It measures how fast your website loads when a user opens it for the first time. This is because most web data is downloaded, extracted, or executed when a website loads for the first time for a unique visitor. The lower this number (less than 100 milliseconds), the better because it means your website has the shortest delay when it loads for the first time.
CLS (Visual Stability)
CLS Stands for Cumulative Layout Shift. CLS is the unexpected shift of website elements while the site is loading. Web elements that shift are visuals, contact forms, website content, font styles, buttons, and videos. Reducing CLS for your site(less than 0.1) is important because no one likes a swaying button and floating text.
2. Page Speed
The second most crucial Google ranking factor for On-page SEO is page speed. Google prefers web pages that load under two seconds – now that’s fast!
This is because Google wants websites with optimized images, content, and layout. Anything that’s out of proportion, too heavy, chunky, or not optimized will cause your site to slow down. This ultimately affects user experience because web visitors don’t like to wait for sites to load.
Optimizing page speed isn’t as challenging as some would assume. In fact, you can run your website on Google’s page speed checker. Here’s what an optimized page looks like.
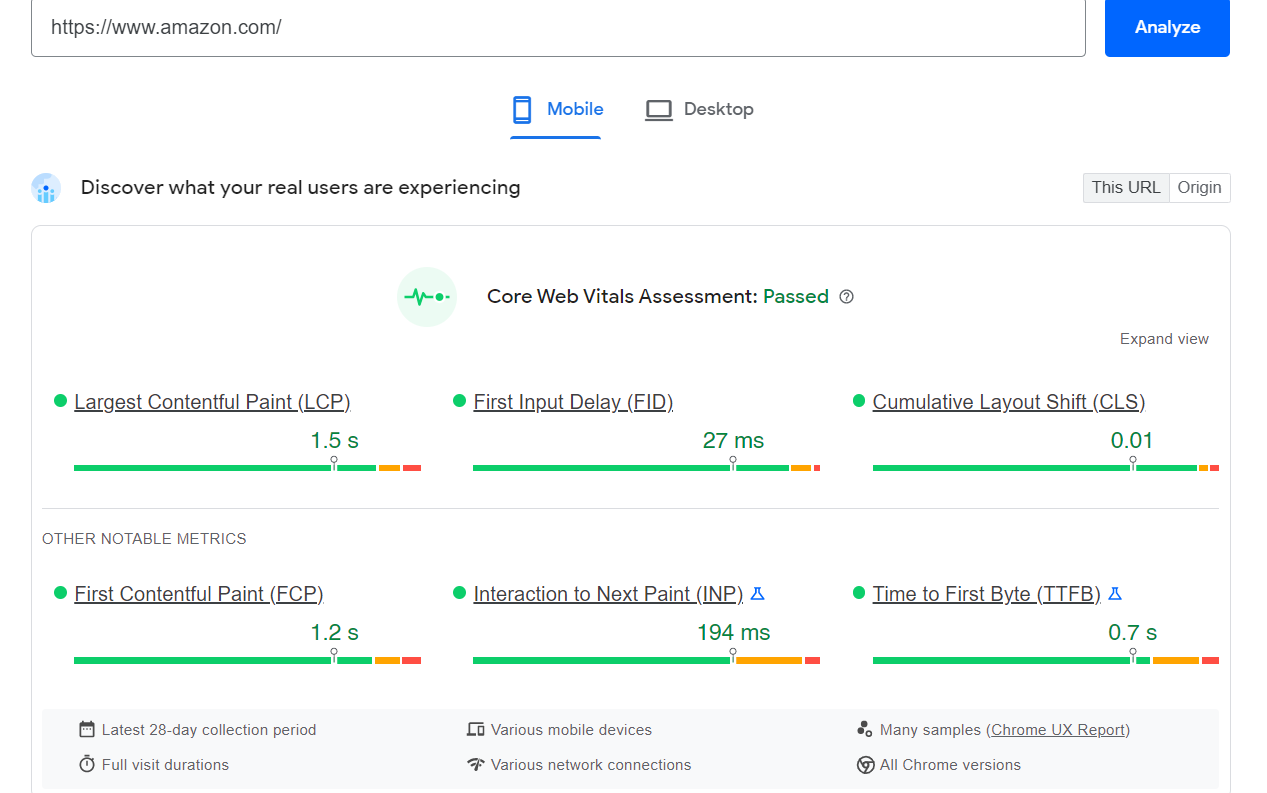
Besides the top core web vitals, you can see 3 more metrics in the Google page speed tester. Optimize these metrics, and your site is most likely to rank higher in search results.
FCP (First Contentful Paint)
FCP is a metric that measures your site’s load speed by recording the time it takes to load its first content. The recording time starts when the site starts to load and doesn’t stop until the first element is loaded.
For this metric, Google refers to the content, images, videos, and other elements that consume web visitors’ internet speed.
FCP is different from LCP in terms of loading elements. For instance, the latter focuses on the largest content file’s loading time, while the former concerns your page’s loading speed from when it starts loading.
INP (Interaction to Next Paint)
INP measures the responsiveness of your site throughout its lifecycle. This is because most of our time is spent on a page when it’s fully loaded. So assessing the responsiveness of your site after the user has landed becomes a part of Google’s analysis for ranking.
Luckily INP is an experimental metric, so I believe it doesn’t affect your ranking as much. But, keeping your page lag-free is key to ranking on Google; if INP is measuring it, you best make sure your INP rating is good. Speaking of which, a good INP score should be low, so the lower your INP, the better.
TTFB (Time to First Byte)
Time to First Byte is a metric that measures the time from connecting with the hosting server to downloading web content. In other words, TTFB measures the responsiveness of your website in terms of connectivity. The faster your site connects with the hosting server, the better. Therefore, this number should be under 100ms.
3. Content
You’ve heard this several times that Content is king. But how does it affect your on-page SEO? Well, SEO without content is a mobile phone without a SIM card. It might look pretty, but it won’t connect you with anyone.
Google has several content metrics to determine if your site is worth ranking. Here are some of those on-page content ranking factors you need to consider to boost your rankings.
E-A-T
Google is hungry for content, but the search engine giant is a picky eater. You can’t post random stuff on your blog page and expect to rank.
Moreover, Google values its user experience, which depends on all the sites ranking on Google’s platform. To avoid a bad user experience, Google ranks content based on E-A-T, which stands for Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness.
Just to be clear, E-A-T is not a ranking factor. It’s a measure of your content’s worth in Google’s eyes. Though it won’t directly impact your search rankings, it plays a crucial role in building your site’s worth among web visitors and search engines.
Keyword Optimization
Whether a web page or a blog post, keyword optimization is the most basic part of on-page SEO. Using keywords in question form and within the first 100 words of your content most likely boosts your search rankings.
Sometimes, it’s easy to determine whether your content is optimized for on-page SEO. For example, if you are optimizing an automobile website or blog post, use keywords like “engine and transmission.”
Long-tail keywords also play a crucial part in ranking your content. Continuing the same example, keywords like “five-speed transmission” or “cars under $20,000” can help your content rank on search results.
Internal Links
Internal links are a vital part of on-page SEO, signaling that your site has more relevant content. Moreover, internal linking is used for passing link juice to other pages on your site.
For instance, if one of your blog posts ranks for a keyword, you can link it with other blogs on your website to pass link juice, traffic, and other page ranking factors.
Tag Optimization
Meta tags help search engines understand your content. Moreover, these tags serve as a means of attracting search visitors to your site. For example, including keywords in your meta title tells Google what your content is about.
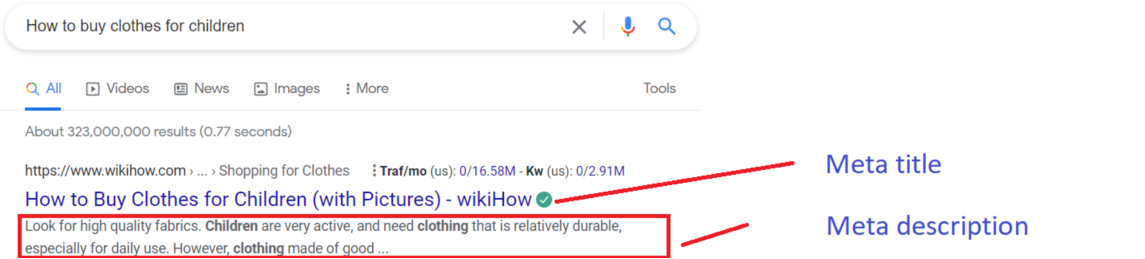
A meta description is a brief explanation of your content. Adding keywords to this description improves your search rankings. Moreover, you can write a creative description to make visitors click on your link.
Image Tags Optimization
Adding images to your blog post or web content is more than improving your site aesthetics. From a technical point of view, images play an important role in SEO if they are optimized.
Adding SEO-friendly alt text, you optimize your images to show up on Google image search against your target keywords.
When an image of your blog or web page is displayed on Google’s image search, it pulls your blog post, and visitors can access your blog through the Google image search as well.
In addition, choosing the right image size and format is key to reducing your site’s load time. Using JPEG images and optimizing them for mobile users improves your on-page SEO.
What is Off-Page SEO?
Off-page SEO refers to all the actions taken outside your website to improve search rankings, web authority, and trustworthiness. Off-page SEO includes various activities, some of which are mentioned below.
- Link Building
- Google My Business
- Reviews
- Social Signals
These off-page SEO activities improve your site’s search ranking, social image and win your business more leads. But executing these off-page SEO activities isn’t as easy as it seems. Here’s our Off-page SEO checklist you can use to improve your ranking efforts.

Google Ranking Factors for Off-Page SEO
Google uses several factors to rank your website. These factors influence your off-page SEO. While each factor can be tackled with a different strategy, they all accomplish a singular purpose – boosting your site’s authority and reputation.
Amongst hundreds of ranking factors, I have listed the top most important Off-page SEO ranking factors.
1. Link Building
Link building boosts your site’s domain authority, ranking, and brand awareness by acquiring juicy backlinks from other reputable sites within your industry. When these high authority sites link back to your website, they signal that you are a trusted business.
A good analogy of how this works can be taken from an example of your friend introducing you to a new person. You’ll automatically trust the other person because that person was introduced to you by someone you knew.
Google search works on the Page Rank algorithm, which looks at the quality and quantity of backlinks. However, the process of link building breaks down into several practices. Here are some of them listed below.
- Guest blogging
- Broken link reclamation
- Infographics distribution
- Social Media links
2. Guest Blogging
Guest blogging refers to posting guest articles on websites to build web authority and contribute something valuable to the publishing site. You get either get a Do follow or a No Follow backlinks in this process.
Do follow links pass Page rank to the website it’s linking to and no follow doesn’t. However, No follow links work as a means of boosting your brand awareness. These links are clickable, like Do follow links, allowing readers can access your website.
3. Broken Link Reclamation
If you are too busy to write guest posts, you can use the broken link strategy to gain valuable backlinks. However, this strategy doesn’t work well for new businesses because you might not have enough links distributed across the internet.
Broken link building works by reclaiming the links you previously had. More often than not, links get broken because your publishing site moved your content to a different page or any other reason.
You can find broken links by pasting your site’s URL on Ahrefs broken link checker tool. Here’s what it looks like.
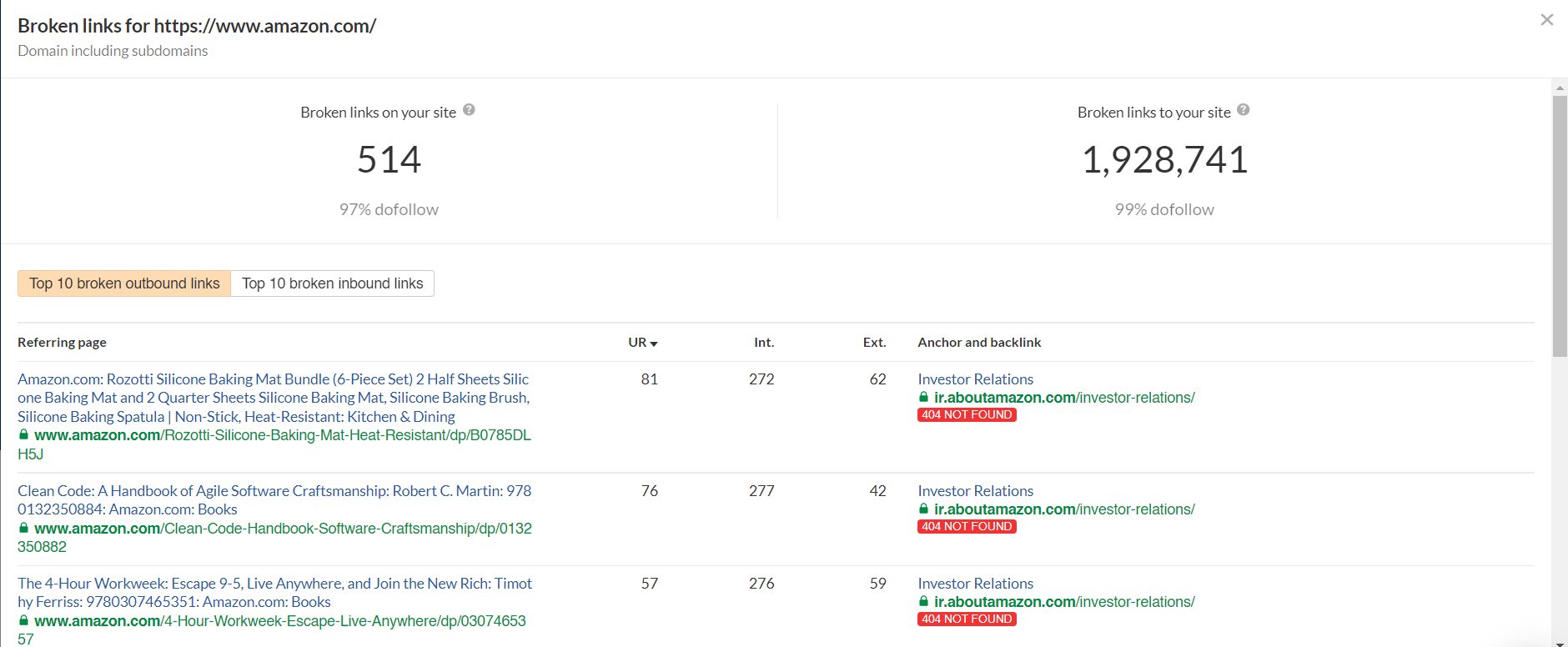
This shows a list of links that are broken, and you can reclaim them by connecting with these sites.
Moreover, you can fix broken links on your site as well with the help of this free tool – but it falls under on-page SEO practices.
4. Infographics Distribution
Businesses are actively looking for niche-relevant stats to post on their website. You can satisfy this need by creating infographics, posting them on your blog page, or listing them on infographic directories. Sites looking for this information will link back to your infographic, automatically earning you a backlink.
Although you can’t control the quality of backlinks you get through infographics, it’s an excellent passive link-building strategy on its own.
5. Social Media Links
You can post your content on social media for a No follow backlink. Although it won’t pass any link juice, you’ll expose your content to a wider audience – boosting your brand awareness.
Social media links work best when you write a killer content piece because it has a chance of going viral. When your followers share your content on their social media page, you get more traffic which can be directed to other web pages or blog posts on your site through internal linking (mentioned in on-page SEO)
6. Google My Business (GMB)
To rank for local search queries like “carpenter near me,” you must create your Google my Business profile. But setting up your GMB profile is only the beginning of your off-page SEO efforts. You must optimize your GMB profile to rank in Google’s “snack pack” results.
Snack pack results are a collection of top GMB profiles that show up against a local keyword like “clothing stores near me.” Here’s what it looks like,
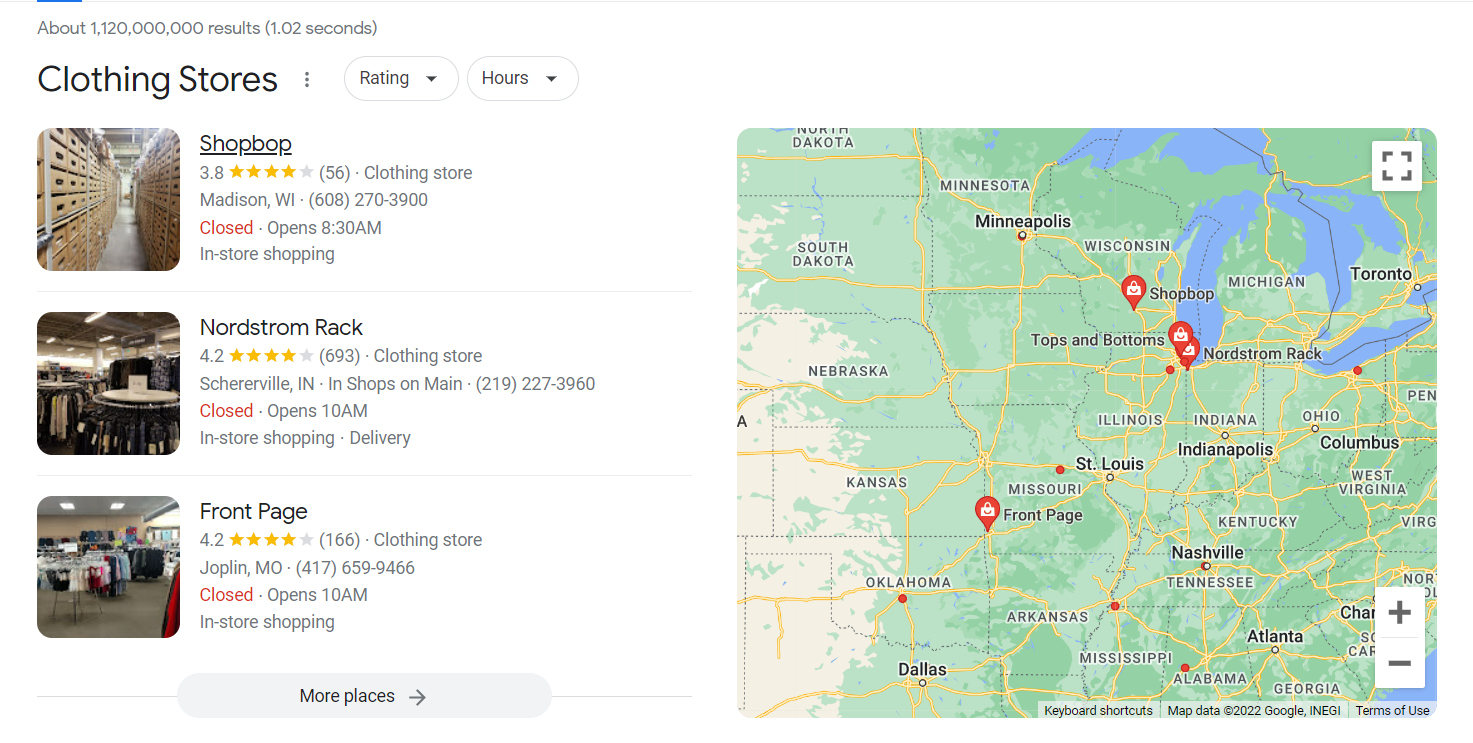
Adding keywords that best represent your business and choosing the right business category increases your chances of ranking in Google’s snack pack results.
And according to Social Media Today, 46% of all Google searches consist of users looking for local results. Hence, GMB optimization is crucial for off-page SEO because it boosts your web traffic and brand awareness in local searches.
7. Reviews
What’s the first thing you do when you are interested in buying a product or service? – Read reviews, right? So does Google – well, not “technically read.”
Reviews are a crucial part of off-page SEO and improve your Google snack pack ranking. This is because Google ranks businesses with high positive reviews, and negative reviews adversely affect your ranking. However, reviews on your personal site aren’t as important as Google reviews.
So fine-tune your services and deliver the best results to your customers, and they’ll be happy to review your services.
Wrapping It Up
SEO can be broken down into two categories – on-page SEO and off-page SEO. Although both categories perform different activities, the end goal is the same – ranking higher on search engine results.
Some marketers value off-page SEO over on-page SEO. However, improving the internal elements of your website is equally important as improving external elements.
If you are looking for an SEO agency to handle both off-page and on-page SEO, you can reach out to Search Berg. Or you can give us a call by dialing 855 444 4777.