Surviving the Cyber Storm: Addressing Critical Cybersecurity Issues for Online Businesses

Would you ever leave your house unlocked while you run errands? Or leave your kids unattended at a store? Or park your car in a questionable neighborhood?
It’s safe to say that nobody would take these risks. So why would you leave your online business unprotected?
If this analogy hasn’t quite hit home yet, let’s look at the statistics.
If a cyberattack comes knocking at your door in 2023, your reputation, finances, operations, legal and regulatory compliance, supply chain, and customer trust will take a hit.
We’re only scratching the surface here.
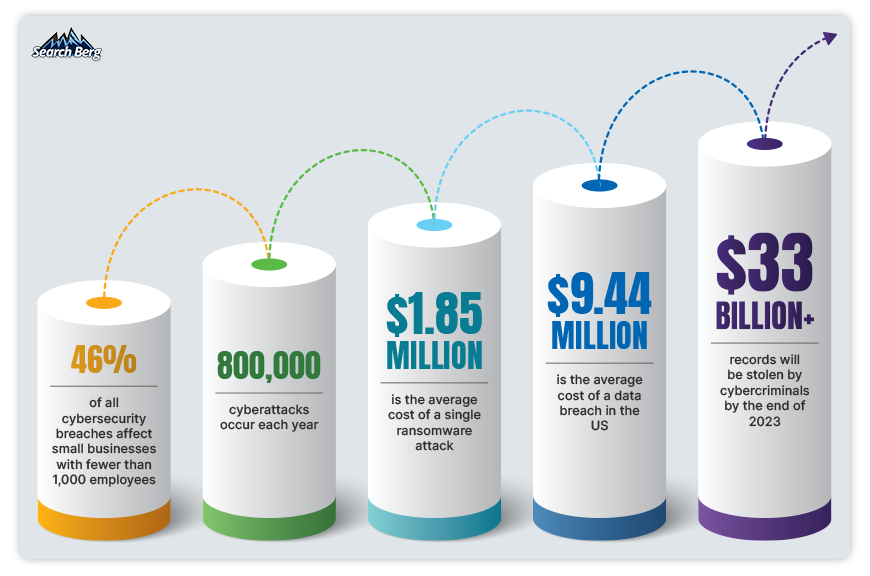
60% of companies don’t just face temporary loss here and there but go out of business entirely following a cyberattack. If you haven’t rolled out a robust cybersecurity plan yet, you’re skating on thin ice.
That’s okay. We’re starting our rescue efforts in this blog.
Let’s take a closer look at the top cybersecurity business issues for 2023. We’ll help you understand the most common yet critical cyberattacks and circumvent them like a seasoned pro.
Let’s begin!
1. Cybersecurity for Small Businesses: The Basics
“My business has never been attacked before. Why should I invest in cybersecurity?”
Great question.
Cyberattacks can never be anticipated. Some of the most notable companies have fallen victim to security breaches, including Twitter, Google, Apple, Target, Ferrari, Yahoo!, AT&T, UPS, Home Depot, and eBay, among many, many others (more on this later).
Most of these companies already had robust cybersecurity plans in place. However, they still managed to get caught in the cyber storm. If a business hasn’t taken any measures to protect itself, you can imagine how debilitating the damage will be.
When a company loses revenue, recovery is often impossible unless they take out a big loan. This isn’t easy territory for a small business that hasn’t found its footing yet.
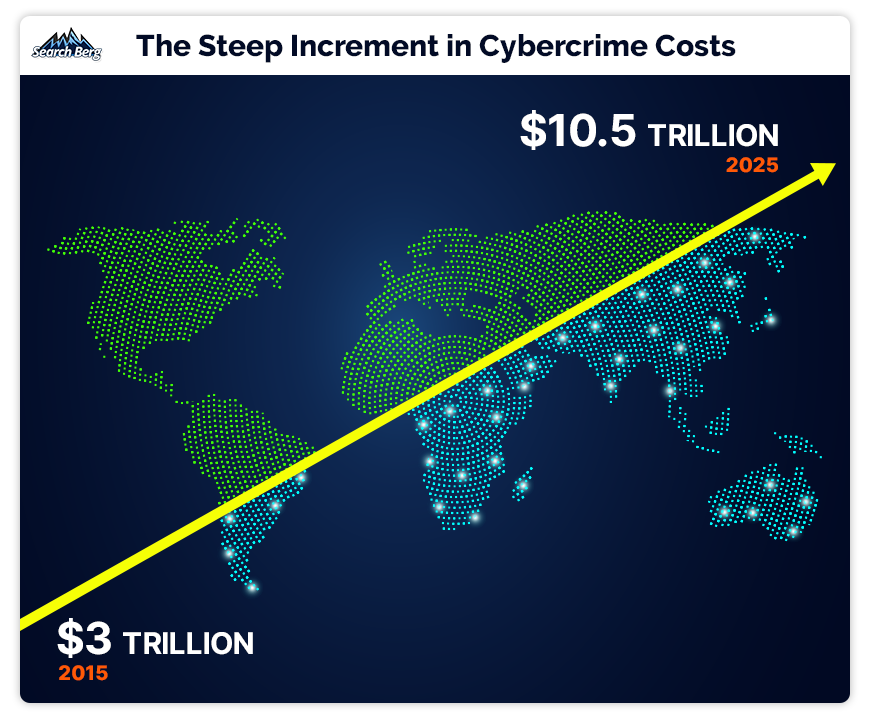
As the cost of cybercrime reaches new heights, small businesses are forced into a corner they can’t back out of.
Cybersecurity helps small businesses protect themselves from cyber threats like malware, ransomware, phishing attacks, and data breaches. You’ll manage to protect sensitive data, including customer information, financial records, and intellectual property.
In 2023, small businesses must comply with various industry-specific regulations and data protection laws (GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, etc.). When you check the cybersecurity box off the list, you’ll also manage to ensure compliance and avoid potential fines, penalties, and legal liabilities.
To put it very simply, a strong cybersecurity plan is your golden ticket to keeping your business up and running. If you’re investing heavily in SEO, your money shouldn’t go down the drain. Cybersecurity will keep you afloat.
It’s important to note that cybersecurity isn’t a magic pill that’ll make all your problems disappear. While it’ll help you avoid a lot of thorns in your path, it won’t remove them from your path entirely.
The cyberspace is incredibly charged; individuals and organizations are continually looking for ways to steal information and infect systems. Protection is important and very much possible. However, complete avoidance is wishful thinking.
As a small to medium-sized business, you should have a razor-sharp focus on minimizing risk, not avoiding it altogether. If you chase perfection, you’ll end up driving your business into a wall.
2. Examples of Notorious Cyberattacks
2.1. The 2020 Twitter Account Hijacking

Picture this. You’re scrolling through your Twitter feed and you suddenly see a tweet from Elon Musk or Jeff Bezos promising to double any Bitcoin sent to a specific address. Sounds too good to be true, right? Precisely, but that’s not what people thought back then.
On July 15, 2020, some of the world’s most influential people’s Twitter accounts were hacked in a brazen cyberattack that left everyone questioning their online security. The victims? Barack Obama, Joe Biden, Bill Gates, Apple, and many more high-profile accounts. A total of 130 accounts were targeted.
The hackers were able to manipulate and deceive certain employees until they gained access to Twitter’s internal systems and tools. They initiated the attack by using social engineering techniques (phishing and pretexting) to trick Twitter employees into revealing their login credentials and providing direct access to internal tools.
In this case, the hackers focused on employees who had access to account support tools. Once they got their hands on the necessary credentials, they used Twitter’s internal tools to bypass account security measures (two-factor authentication, for one) and take control of the targeted accounts.
The damage? Unsuspecting users who fell for the scam sent Bitcoin to the provided address, hoping to receive double their investment in return. The attackers were able to collect more than $100,000 worth of Bitcoin.
After the attack became evident, Twitter took swift action to contain the breach. The company temporarily prevented verified accounts from tweeting, reset the passwords of affected accounts, and launched an internal investigation.
Twitter’s 2020 hack highlights the critical importance of employee training, strong security practices, and constant vigilance against potential threats. If you let even the smallest mistake slip through the cracks, your business will get exposed to a plethora of cyberthreats.
2.2. The 2021 Microsoft Exchange Server Data Breach

Microsoft, one of the world’s most powerful tech giants, faced a sophisticated cyberattack that sent shockwaves across the globe.
You wouldn’t expect one of the biggest players in the tech industry to get defeated at a game they excel in. But that’s exactly what happened.
This is a chilling reminder that even tech businesses aren’t immune to cyberthreats.
In March 2021, a group of skilled hackers exploited vulnerabilities in the Microsoft Exchange Server, an email platform used by countless businesses worldwide. They were able to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data.
The attackers started reading emails, exfiltrating data, and even installing malware for future attacks. The scale of the breach was enormous. Tens of thousands of organizations, small businesses, governments, and nonprofits were affected.
Microsoft’s security team identified the vulnerabilities being exploited, publicly disclosed them, and released emergency security patches. They urged customers to apply the updates immediately to protect their systems from further exploitation.
Microsoft also worked closely with cybersecurity experts, government agencies, and industry partners to investigate the attack and share critical information about the attackers and their techniques.
Had both Twitter and Microsoft not rolled out a robust contingency and mitigation plan on time, the damage would have been worse. They were able to do this because they already had a cybersecurity plan in place.
Over the years, countless companies have suffered the consequences of leaving their data and systems unprotected. Explore these cyberattacks in detail:
- Yahoo Data Breach
- Apple XcodeGhost Malware Attack
- Equifax Data Breach
- Target Holiday Shopping Cyberattack
- iCloud Data Breach
- Sony Pictures Data Breach
- JPMorgan Chase Cyberattack
- SolarWinds Supply Chain Cyberattack
- Colonial Pipeline Ransomware Attack
- eBay Cyberattack
- Mailchimp Cyberattack
Now that you have a more nuanced understanding of the nature and criticality of cybersecurity, let’s dive into the most common yet critical cybersecurity issues for small businesses in 2023.
We’ll explain each danger zone with examples to help you understand how it applies to your business. We’ll also offer an in-depth look at the right way to prevent and solve cybersecurity issues.
Let’s begin!
3. Cybersecurity Issues in Business
3.1 Phishing Attacks

Picture this.
You run Fiona’s Fits, a lovely little online boutique for young women. One day, you receive an email from a “supplier” asking you to update your payment information. Sounds pretty harmless, right?
Turns out, the “supplier” is actually a cybercriminal, and the seemingly innocent request is a phishing email designed to steal your credentials. In a rush to get things done, you comply, and the attackers get hold of your financial data. Your business has just been added to the list of millions of phishing attack victims.
A phishing attack is a type of cyberattack that involves a high level of deception. Cybercriminals hatch carefully constructed plans to deceive individuals or businesses into revealing sensitive information (usernames, passwords, credit card details, and other personal data).
This is usually done by masquerading as a trustworthy entity through email, social media messages, or text messages.
“How on earth do people end up falling for this?”
Cyberattackers are adept at mimicking the appearance and tone of legitimate organizations (banks, online service providers, colleagues, and even friends). The message also typically contains a convincing call-to-action (CTA) that urges the recipient to click on a link, download an attack, or provide sensitive information directly.
Once the target takes action, their sensitive information is sent to the attacker, who then uses it for fraudulent activities, identity theft, or unauthorized access to the victim’s accounts.
Acorn Financial Services, Twilio, Allegheny Health Network, and Mailchimp are a few of the many businesses that fell victim to costly phishing attacks in 2022-2023.
It should come as no surprise that phishing is the most common cybersecurity issue today
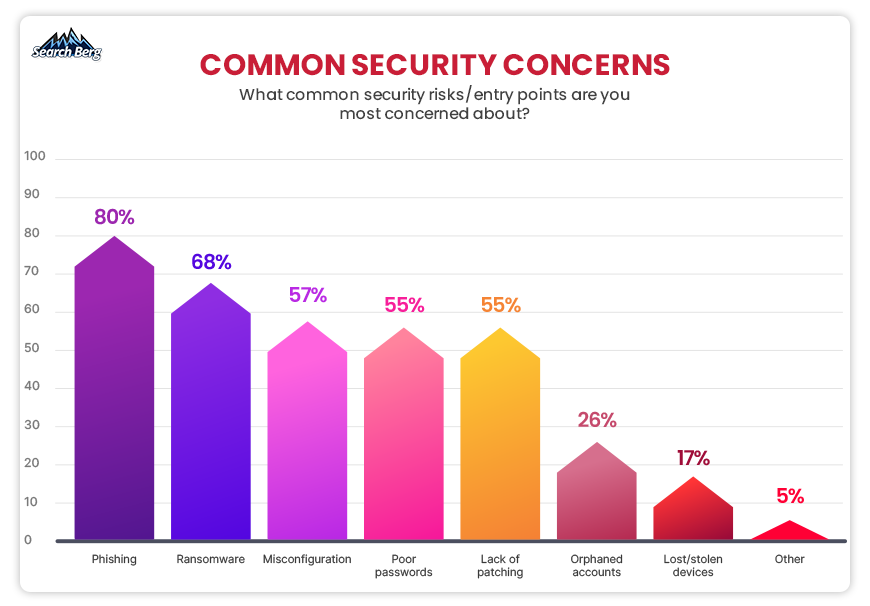
Source: Fortra’s 2022 Pen Testing Report
Phishing attacks are incredibly common because they rely on social engineering and manipulation to exploit human vulnerabilities rather than targeting technical weaknesses in a system.
As a small business, you already have limited resources to begin with. If you fall victim to a phishing attack, you’ll face significant financial loss.
Attackers can use stolen financial information to make unauthorized transactions or even steal funds from business bank accounts. This can be especially devastating for small businesses that operate on tight margins.
If a phishing attack succeeds, it can lead to a data breach. If sensitive business information or customer data is stolen, you’ll face legal liabilities and reputational damage.
Your business may be forced to shut down.
Prevention & Solution
Refer to the example we shared earlier. Here’s what Fiona’s Fits should have done to avoid falling for this scam.
For starters, they should have trained employees to identify phishing emails. Employees must be adept at identifying odd email addresses, poor grammar, and unsolicited requests for sensitive information.
Additionally, enabling two-factor authentication (2FA) on all accounts is imperative. This adds an extra layer of security (even if attackers get hold of your credentials).
To nip phishing emails in the bud, Fiona’s Fits should have used an email filtering tool to block spam and phishing emails.
While rolling out a good prevention plan is important, it’s not enough. If you end up falling victim to a phishing attack, you should be able to mitigate the potential damage and act promptly.
Start by identifying the attack. Verify that the incident is indeed a phishing attack.
If the attack is ongoing, try to contain it by blocking the sender’s email address, updating spam filters, and notifying employees about the situation to prevent further incidents.
Follow this up by reporting the attack to your IT department or security team so they can take further action, i.e., contact law enforcement or regulatory bodies.
Determine the extent of the damage by identifying which employees have been affected, what data has been compromised, and which systems (if any) have been breached.
Remediate the damage by resetting passwords, implementing additional security measures, or even restoring systems from backups if necessary.
At this point, your company should know exactly what is going on. Inform employees, customers, and stakeholders about the incident, roll out training plans, conduct a thorough post-incident analysis, and stay vigilant in the future.
3.2. Ransomware Attacks

Let’s consider an example.
You run an online bookstore, Novel Nook. All of a sudden, your systems get locked down. The attackers demand a hefty ransom to decrypt your store’s data. Left with no choice, you comply, losing both money and trust from customers.
This is a ransomware attack in a nutshell.
In 2022, there were 236.1 million ransomware attacks on businesses. In 2023, this number is expected to increase significantly.
A ransomware attack occurs when a hacker or group of hackers use malicious software to encrypt a company’s data or computer systems, effectively locking the company out of its own data.
A ransomware attack is the most frustrating and damaging attack for small businesses in 2023.
Let’s say your business falls victim to a ransomware attack. If you don’t have adequate data backups, you’ll be forced to pay a ransom to regain access to your data.
This is where things get tricky.
Even if you pay the ransom, there’s no guarantee that the attackers will give you the decryption key. In some cases, the decryption key has malware or other malicious code, which ends up causing more harm.
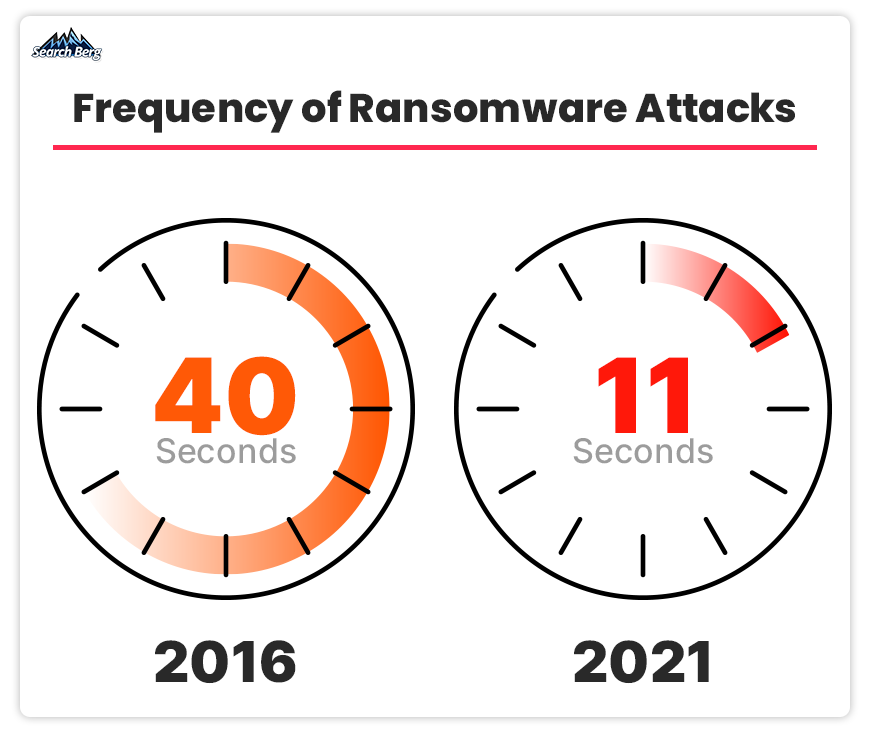
Source: Cybersecurity Ventures
Prevention & Solution
As disastrous as a ransomware attack is, prevention is a piece of cake (provided that you use the right game plan). Use a multi-layered approach that combines technical and human measures. Follow these practices:
- Keep Software and Systems Up-to-Date: Ensure that all software and systems are up-to-date with the latest security patches and updates. This will help prevent attackers from exploiting known vulnerabilities.
- Use Antivirus Software and Firewalls: Install and maintain antivirus software and firewalls to protect your systems from known threats. These tools must be configured properly and updated.
- Conduct Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in your systems. Address all issues promptly.
- Implement Access Controls: Implement access controls to limit who can access sensitive data and systems. Make sure employees only have access to the data and systems they need to do their job.
- Use Backup and Disaster Recovery Solutions: Regularly backup all data to an offsite location and ensure that backups are tested regularly. This will help you restore data in the event of a ransomware attack.
- Train Employees: Educate your employees on how to recognize and avoid phishing attacks and provide training on best practices for cybersecurity. Ensure that employees know how to report potential security incidents.
- Implement Least Privilege: Use the principle of least privilege to limit employee access to sensitive systems and data.
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication: Use multi-factor authentication to require more than one form of identification before allowing access to sensitive data or systems.
- Monitor for Suspicious Activity: Monitor your systems for suspicious activity and unusual network traffic. Implement intrusion detection and prevention tools to detect and prevent attacks.
- Prepare an Incident Response Plan: Have an incident response plan in place in case of a ransomware attack. The plan must include procedures for containing the attack, notifying relevant parties, and restoring systems and data.
3.3. Weak Passwords

Let’s consider the example of a small family-owned design business that recently expanded its online presence by launching a website for online orders.
The business owner, being unfamiliar with cybersecurity best practices, ends up using the same weak password (“restaurant123”) for all online accounts, including email, the website’s admin panel, and the point-of-sale system.
A week later, a cybercriminal stumbles upon their website and decides to run a password-cracking tool to see if they can gain access to the admin panel. Sure enough, they can. To their delight, the weak password was easily cracked, granting them access to not only the website but also the restaurant’s entire digital infrastructure.
The attacker could view sensitive customer data, including names, addresses, and credit card information.
The breach goes unnoticed until customers begin reporting fraudulent charges on their credit cards, tracing the source back to the design business. The business is forced to inform its customers of the breach, resulting in a significant reputational loss.
This is the consequence of setting weak passwords. Over the years, several established businesses like Microsoft, Ticketmaster, DailyQuiz, Verkada, and GoDaddy have faced debilitating password breaches.
Weak passwords are a gateway to unauthorized access to your systems and sensitive data. Many small businesses overlook the importance of strong password policies, which makes it incredibly easy for attackers to gain entry.
Prevention & Solution
To safeguard your small business from weak password-related cyberattacks, roll out the following action plan:
- Strong Password Policy: Set up a password policy that requires the use of strong, unique passwords for all accounts. Use a minimum of 12 characters, include a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, use numbers, and include special symbols. Avoid using easily guessable information like names, dates, or common words.
- Password Rotation: Regularly update and change passwords for all accounts to minimize the risk of unauthorized access. Set a schedule for password rotation (e.g., every 60 or 90 days) and enforce this policy for all employees.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enable multi-factor authentication on all accounts and systems where possible.
- Password Managers: Encourage the use of password managers to help employees securely store and manage their passwords. Password managers generate complex, unique passwords for each account and store them in an encrypted vault, reducing the likelihood of weak passwords and password reuse.
- Employee Training: Plan regular training and awareness programs for employees, emphasizing the importance of strong password practices and the risks associated with weak passwords. Educate them on how to create secure passwords and the consequences of password-related cyberattacks.
If you’ve already fallen victim to a password breach, immediately change the weak passwords on all affected accounts and systems to strong, unique ones. Your employees must do the same for their accounts.
Temporarily disable any compromised accounts and limit access to sensitive systems until the situation is resolved. Follow this up by examining logs and other data to determine the extent of the breach.
Keep an eye on your accounts and systems for signs of unauthorized access or malicious activity. If the damage is too deep, turn to cybersecurity professionals for help.
3.4. Insider Threats

A disgruntled employee at a small legal firm decides to leak sensitive client information to a competitor. The outcome? The agency’s reputation and future business prospects are ruined overnight.
This happens all the time, especially in the startup and small business landscape. Approximately 2,500 internal security breaches occur daily in the United States.
Insider threats are cybersecurity risks that come from within your organization. Intentional or accidental, these threats can have serious consequences. The culprit may be an employee, contractor, or partner who has access to your systems and data.
As a small business, you may build a tight-knit community of employees and managers. However, this doesn’t mean you extend the courtesy of trust to everyone.
Corporate relations can change within a matter of minutes, leaving your business vulnerable to a possible attack from someone you wouldn’t have suspected otherwise.
Keep an eye out for the five main types of insider cyberattacks:
- Data Theft or Leakage: Insiders may steal sensitive information (e.g., intellectual property, financial data, customer information, etc.) for personal gain or cause harm to the organization. This information is sold to competitors or on the dark web or used for identity theft and other fraudulent activities.
- Sabotage: Disgruntled employees or those with malicious intentions may intentionally damage or disrupt an organization’s systems, networks, or data. This may include deleting critical files, introducing malware or viruses, or causing system outages.
- Fraud and Financial Crimes: Insiders with access to financial systems may commit fraud or embezzlement by manipulating financial records, creating fake transactions, or misappropriating funds.
- Espionage: Insiders may engage in corporate espionage by providing sensitive information or trade secrets to competitors, foreign governments, or other external entities.
- Unauthorized Access and Privilege Abuse: Insiders may abuse their access privileges by accessing sensitive information or systems without authorization or for purposes beyond their job responsibilities. This can lead to data breaches or other security incidents.
Prevention & Solution
Let’s be honest. In most cases, there’s only very little you can do to prevent insider threats.
No matter how careful you are, your current employees will have access to basic information about your business. And no matter how thoroughly you vet them, you’ll fail to pick up on the subtleties.
This doesn’t mean you shouldn’t roll out a cybersecurity plan for insider threats. It just means that prevention may not always be possible.
Use a combination of technical, administrative, and human-centric strategies to protect your business from insider attacks. We recommend the following game plan:
- Access Control: Implement role-based access control (RBAC) to ensure employees only have access to the data and systems necessary for their job. Regularly review and update user access privileges, especially when employees change roles or leave the organization.
There’s only so much you can do here. Your employees will still have access to a lot of critical data, no matter how much you limit their access. A certain level of risk will always linger.
- Monitoring and Auditing: Monitor user activity on your systems and networks. Look for unusual or suspicious behavior that indicates a potential insider threat. Regularly audit access logs, security incidents, and data usage to identify any patterns or inconsistencies.
- Background Checks: Perform thorough background checks on new hires, contractors, and business partners to identify any potential risks. This must be done before you grant access to sensitive information and systems.
Always verify the applicant’s identity using government-issued identification documents, review their criminal history, scan their employment history, confirm their claimed educational degrees/certifications/professional licenses, conduct credit checks, and check their social media pages.
- Clear Policies and Guidelines: Establish clear security policies and guidelines that outline the acceptable use of company resources, data handling procedures, and the consequences of policy violations. Your employees must be aware of these policies and understand their responsibilities.
- Positive Work Environment: Foster a positive, supportive, enriching, and encouraging work environment. Support employee well-being, encourage open communication, and address grievances or concerns promptly. A satisfied workforce is less likely to engage in malicious activities against a business.
- Exit Procedures: Establish a formal exit process when employees leave an organization. This should include revoking access to systems and data, retrieving company-owned devices, and conducting exit interviews to gather information about potential security risks.
If you’ve already fallen victim to an insider attack, identify the attacker at the earliest, disable their access to systems and data, and reset all passwords and access credentials.
Fire them immediately and interrogate other employees within their work circle to determine if the threat lingers.
After dealing with the insider attack, review and update your incident response plan to incorporate lessons learned and improve your preparedness for future incidents. Your plan must include specific procedures for handling insider threats, including identification, containment, and recovery strategies.
Treat Your Business Like a Baby
Your business isn’t an independent adult, it’s a baby. Instead of letting it march to the beat of its own drum, take good care of it.
Whether you’re investing in SEO services or redesigning your website, make sure you hand your business over to trusted experts who don’t jeopardize your security and safety. Additionally, invest in a robust cybersecurity plan that safeguards your business from all threats, big or small.
In this blog, we walked you through the top cybersecurity issues and solutions.Let us know what you’d like to see from us next!